Answering the Woes of India’s Public Transport Systems
The electric car is often looked upon as a successful measure to reduce emissions and combat climate change. At the recent COP26 summit, governments worldwide pledged to promote the sale of zero-emission vehicles and policies enabling the same by 2035. However, are electric cars really the answer to our predicament? And where is the electricity required to power such vehicles coming?
According to data from a report by the Central Electricity Authority, about 60.2% of India’s energy is generated through fossil fuels, of which 51.9% comes from coal power plants. Therefore, in a country like India, where fossil fuels are the primary source of energy generation, replacing fuel-powered vehicles with electric ones would be hardly beneficial.
Perhaps, the solution lies in reducing the need for privately-owned vehicles and promoting and enabling the use of public transport systems that enhance the citizens’ quality of life.
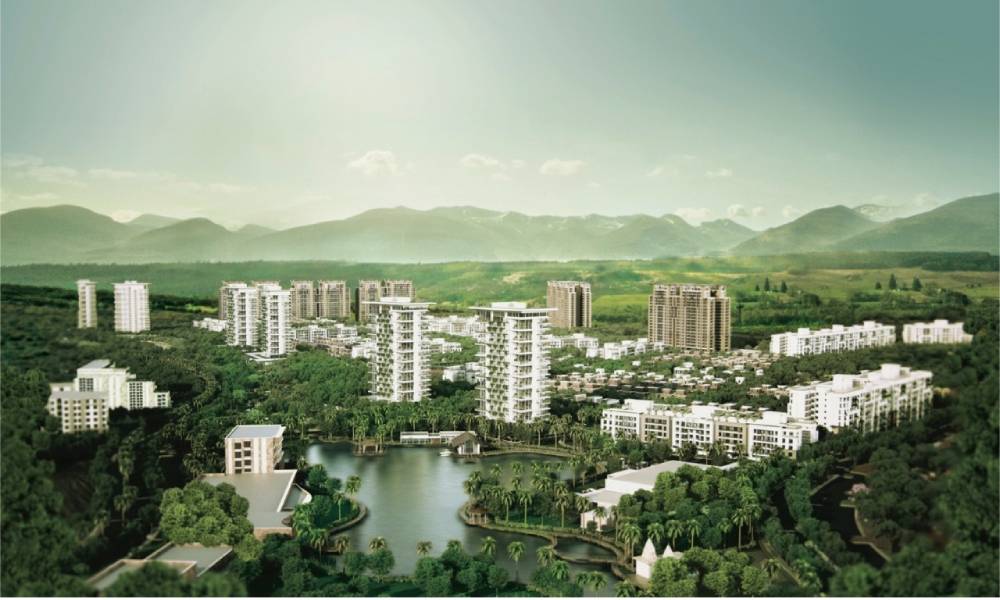

City municipalities and planning bodies must take a step towards implementing policies and investing in the idea of a “15-minute city” [1] – a people-centric concept that advocates for all essential urban services to be accessible within a 15-minute walk. Instead of developing long-term, large-scale land-use plans for cities and towns, it is crucial for planners to develop incremental short-term neighbourhood-level plans that encourage the idea of such 15-minute cities within larger cities. In addition, residential neighbourhoods must evolve to accommodate commercial buildings to bring essential services closer to the citizens. Further, the municipal budget can be decentralised to the neighbourhood-level where the citizens’ needs are prioritised and the people are directly involved through all stages of the planning process.
For instance, The Neighbourhood Plan initiated by the municipal body in Barcelona aims to transform critical issues faced by some of the city’s most disadvantaged neighbourhoods across various domains such as education, public health, housing, community action, public space, accessibility, etc. in congruence with the community over three years between 2021-2024. Previously, The Neighbourhood Plan 2017 saw the improvement of sixteen such neighbourhoods, which significantly enhanced the lives of its citizens by generating employment opportunities, improving pedestrian infrastructure, elevating education and public health within the neighbourhood, and encouraging citizen participation in the planning process, over the course of three years.
In most Indian cities, the working class – which makes up the majority of the population – walks to work. In fact, due to the high costs of long-commuting, most of the working class prefers living within walking distance to their workplace. In Mumbai alone, about 1.5 crore people walk to work -- a report by Mumbai Vikas Samiti, a think tank, states that nearly 60% of daily commuters in Mumbai prefer walking while travelling to their workplace – especially to and from railway stations. In fact, car ownership in Mumbai continues to be the lowest amongst the Tier 1 cities of India.[2] Walkability is, therefore, an excellent urban planning strategy that can significantly reduce energy consumption. Unfortunately, in India today, urban planning focuses on motorised transport systems rather than non-motorised means. For instance, according to the Indian Roads Congress, the clear walking zone of a footpath must be at least 1.8m wide for a road that is broader than 10m [3] – This means that the pedestrian walkway accounts for less than 15% of space in cities where more than half of the population prefers walking over using motorised modes of transport.
Copenhagen is a prime example of a pedestrian-friendly city, which the planners achieved through a tactful 10-step program. [4] The most crucial part of this plan involved turning the city’s main street into a pedestrian-only thoroughfare in 1962. Gradually, this street came to be linked to other pedestrian-only streets, forming a stringent network of walkable pathways within the city – which started allowing cyclists too over time. Today, the citizens are hardly dependent on cars and vastly prefer walking and/or cycling.
Currently, most Indian cities like Mumbai, Chennai, and Delhi have isolated authorities for different modes of public transport like buses and the metro. For example, Brihanmumbai Electric Supply and Transport (BEST) is a civic body that provides public bus services in Mumbai, whereas the Mumbai Metro Rail Corporation (MMRC) regulates the city’s metro rail services. Discrepancies between the two civic bodies would lead to inconsistencies in the overall public transport system, causing difficulties to the commuters. Instead, a unified authority that deals with all modes of public transport ranging from buses to suburban railway and metro can prove to be highly beneficial, as in the case of several cities such as Singapore and Chicago.
The Land Transport Authority (LTA) designs, develops and builds Singapore’s land transport and infrastructure systems to create a people-centric transportation network. Since its inception in 1995, the LTA has changed the face of public transport within the island. Today, it has established over 160km of expressways, a 200km monorail network, 120km of cycling paths, and other alternative means of public transport. [5] The LTA also uses new-age technology to provide maps, transport routes and additional information to the citizens at their fingertips.
As mentioned earlier, car ownership in India stands at about 2-3%. Instead of looking at escalating this figure, we must strive to reverse this number and promote walking and public transport or non-motorised means such as cycles. Urban planning strategies and policies must transpire through an inclusive process that takes into account the needs and aspirations of all the potential stakeholders to enhance connectivity, mobility, and accessibility within the city – this will also drastically reduce energy consumption on a large scale.
- https://www.15minutecity.com/about
- https://wwfin.awsassets.panda.org/downloads/urbanisation_report.pdf
- https://go.itdp.org/download/attachments/60296563/IRC%202012%20%28Guidelines%20For%20Pedestrian%20Facilities%29.pdf?api=v2
- http://www.newurbanism.org/pedestrian.html
- https://www.lta.gov.sg/content/ltagov/en/who_we_are.html